17+Years, More than 25000 Clients and 10000+
agreements drafted
Overview
A Memorandum of Understanding or more popularly known as an MOU is an agreement, which is made between two or more parties, when they wish to lay out the rights and obligations of the parties, and thereby, agree on a course of action to reach a valid and a common conclusion. It is indeed a formal agreement; however, it is not legally binding on the parties. In order to be legally operative, the MOU between the parties should clearly enumerate the name of the parties, the object, and the purpose of the contract, and also summarise all the important terms and conditions. Usually, MOUs are less time consuming, and since it is not legally binding, the parties avoid the legal implications altogether, as opposed to a contract. This is majorly attributable to the fact that a legal agreement between parties contains the undertaking of the risks, warranties, and indemnifications due to the nature of the contract involving the exchange of money or any other considerations. On the other hand, an MOU is a non-binding agreement that highlights the effective negotiations between the parties, that were involved in achieving a shared goal.
What Is The Process?
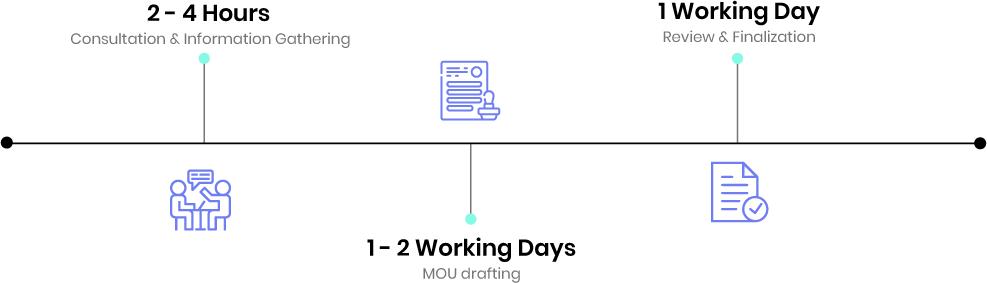
1. Discussion
In order to draft or generate an MOU, the concerned parties should, at the outset, reach a mutual understanding. In this process, each side learns about the things that are mutually required for each party in order to move forward with a synergetic relationship.
2. Drafting
This process often begins when each party drafts its own best-case MOU through a professional.
3. Finalization
The MOU and the process of drafting it to consider all ideal or preferred outcomes. Moreover, it also considers the things that are offered to the other party(s), and what points may be non-negotiable.
Details Required
- Names of parties.
- Specific points of understanding between the parties
- Description of the project
- Roles and responsibilities of each party
Timeline
Testimonials
Get Started
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is an MOU a legally binding document?
Although MOUs aren’t legally binding and are mere understandings between two parties that are legally documented. However, at the same time, if an MOU is drawn up for the exchange of money, it becomes legally binding due to the presence of consideration.
2. Should stamp duty be paid on an MOU?
MOUs, are usually not affixed with stamp duty. However, from a legal standpoint, a stamp duty paid document is considered to have evidentiary value and can be admitted in the court as evidence. Therefore, it is advisable to have an MOU stamped in case an MOU is drawn with respect to immovable property or money as consideration.
3. Why is MOU made if it is not legally binding?
An MOU is made for the parties to document a potential legal obligation in the future.
4. Is MOU enforceable by law?
In general, MOU is governed by the Indian Contract Act, 1872. In case an MOU fulfills the condition of a valid contract, its performance can be specifically enforced under the Specific Relief Act, 1963, where a Specific relief is granted when compensation cannot be ascertained in monetary terms. In cases where an MOU does not fulfill the conditions laid down under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, it cannot be termed as a legally valid contract. However, in any case, it can still be enforced in the court of law based on the principles of promissory estoppel and equity.
5. Which entities can establish Memorandum of Understanding?
- Companies or organizations can execute an MOU to establish partnerships with each other or individuals.
- A Government Agency can execute an MOU with another agency within the same Government or another country’s Government.
- Countries can independently execute an MOU with another country/other countries.
- Individuals with other individuals or company.
- Legal Entities and Trusts
6. What is the purpose of an MOU?
The objective and purpose of having an MOU are to broadly define what a particular agreement would cover i.e. probable outcome of an agreement and its benefits. It defines all the areas that both parties wish and agree to cover in the agreement.
7. What is the duration of an MOU?
Generally, an MOU would last for such a duration that is mutually agreed upon by the parties or is contingent on the happening of a certain event.
8. Are the parties to MOU deemed partners or agents of one another?
There is no such relationship. Each party is independent and responsible for its own actions.























